Book Value Per Share BVPS Formula + Calculator
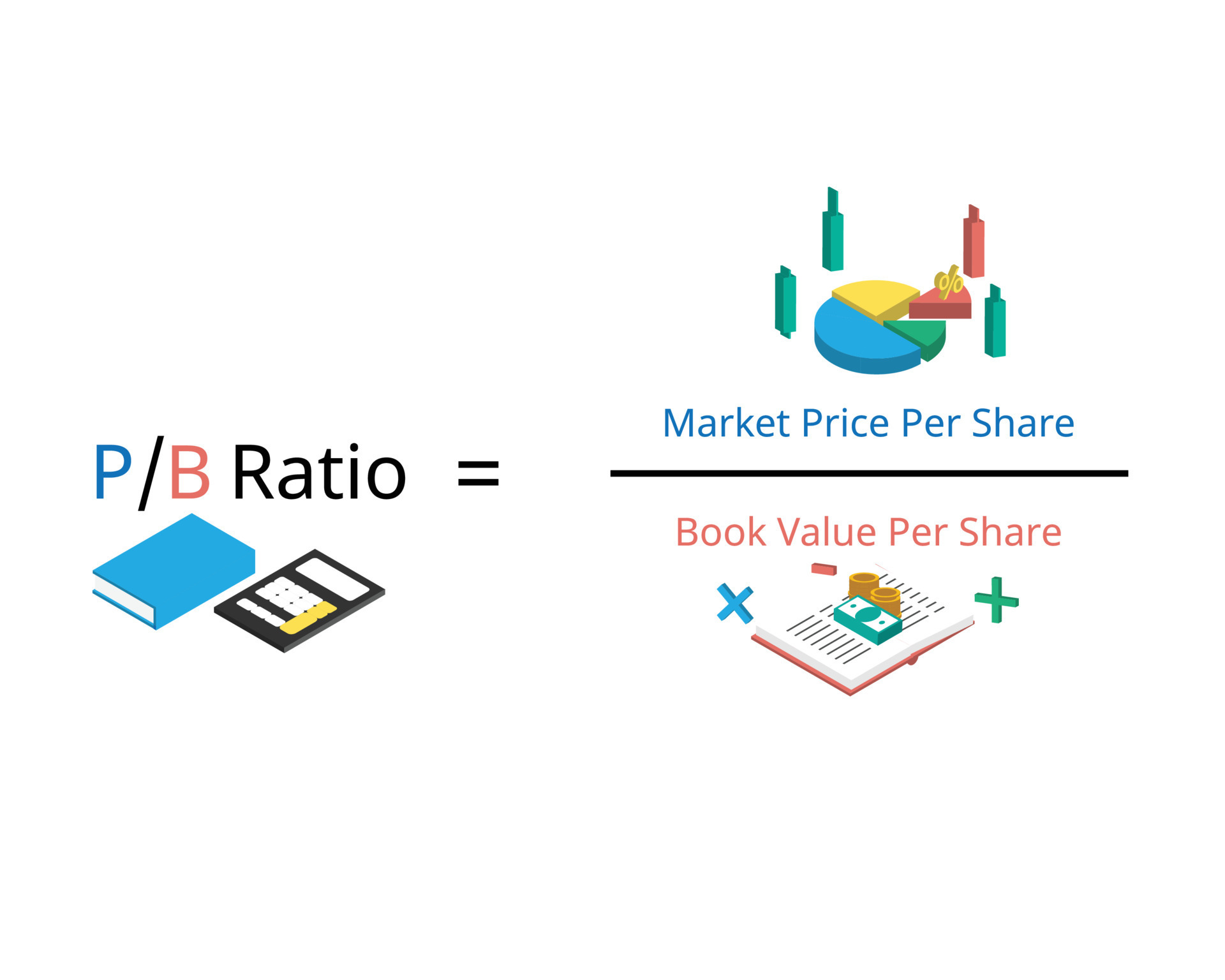
A simple calculation dividing the company’s current stock price by its stated book value per share gives you the P/B ratio. If a P/B ratio is less than one, the shares are selling for less than the value of the company’s assets. This means that, in the worst-case scenario of bankruptcy, the company’s assets will be sold off and the investor will still make a profit.
- There are a number of other factors that you need to take into account when considering an investment.
- The market value per share is a company’s current stock price, and it reflects a value that market participants are willing to pay for its common share.
- To understand what is PB ratio in share market deeply, keep reading this detailed guide ahead.
- Clear differences between the book value and market value of equity can occur, which happens more often than not for the vast majority of companies.
- Now, let’s say that Company B has $8 million in stockholders’ equity and 1,000,000 outstanding shares.
Price-To-Book Ratio
When preferred shares are not present, the entire equity of the stockholders is utilized. It depends on a number of factors, such as the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team. Even if a company has a high book value per share, there’s no guarantee that it will be a successful investment. This is why it’s so important payroll bookkeeping to do a lot of research before making any investment decisions. Preferred stock is usually excluded from the calculation because preferred stockholders have a higher claim on assets in case of liquidation. Despite the increase in share price (and market capitalization), the book value of equity per share (BVPS) remained unchanged in Year 1 and 2.

What Does Book Value Per Share (BVPS) Tell Investors?
It can offer a view of how the market values a particular company’s stock and whether that value is comparable to the BVPS. Book value is the value of a company’s assets after netting out its liabilities. It approximates the total value shareholders would receive if the company were liquidated. BVPS represents the accounting value of each share based on the company’s equity, while the market value per share is determined by the stock’s current trading price in the market.
Advantages of Using PB Ratio
Book value is not very useful in the latter case, but for companies with solid assets, it’s often the No.1 figure for investors. If we assume the company has preferred equity of $3mm and a weighted average share count of 4mm, the BVPS is $3.00 (calculated as $15mm less $3mm, divided by 4mm shares). Price-to-book (P/B) ratio as a valuation multiple is useful when comparing similar companies within the same industry that follow a uniform accounting method for asset valuation.
How to calculate P/B ratio?
The company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, its common equity increases along with BVPS. If XYZ uses $300,000 of its earnings to reduce liabilities, common equity also increases. Calculating a company’s value per share using equity accessible to common shareholders is possible using the book value per share formula. It’s also known as stockholder’s equity, owner’s equity, shareholder’s equity, or just equity, and it refers to a company’s assets minus its liabilities.
How to Calculate Book Value Per Share (BVPS)
Like a person securing a car loan by using their house as collateral, a company might use valuable assets to secure loans when it is struggling financially. The answer could be that the market is unfairly battering the company, but it’s equally probable that the stated book value does not represent the real value of the assets. Companies account for their assets in different ways in different industries, and sometimes even within the same industry. Failing bankruptcy, other investors would ideally see that the book value was worth more than the stock and also buy in, pushing the price up to match the book value.
In closing, it’s easy to see why the book value per share is such an important metric. It’s a simple way to compare the value of a company’s net assets to the number of shares that are outstanding. But be sure to remember that the book value per share is not the only metric that you should consider when making an investment decision. There are a number of other factors that you need to take into account when considering an investment. For example, the company’s financial statements, competitive landscape, and management team.
The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and total liabilities, and not its share price in the market. Assume that XYZ Manufacturing has a common equity balance of $10 million and 1 million shares of common stock are outstanding. This means that the BVPS is ($10 million / 1 million shares), or $10 per share. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases.
A company can use a portion of its earnings to buy assets that would increase common equity along with BVPS. Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also increase its common equity and BVPS. A company’s stock is considered undervalued when BVPS is higher than a company’s market value or current stock price. If the BVPS increases, the stock is perceived as more valuable, and the price should increase. The price of a single publicly traded stock divided by the number of shares outstanding gives us the market price per share. While BVPS is set at a certain price per share, the market price per share varies depending purely on supply and demand in the market.
To obtain the figure for total common shareholders’ equity, take the figure for total shareholders’ equity and subtract any preferred stock value. If there is no preferred stock, then simply use the figure for total shareholder equity. The book value per share (BVPS) ratio compares the equity held by common stockholders to the total number of outstanding shares. To put it simply, this calculates a company’s per-share total assets less total liabilities. Book value per common share (or, simply book value per share – BVPS) is a method to calculate the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders’ equity in the company.
Let’s say that Company A has $12 million in stockholders’ equity, $2 million of preferred stock, and an average of 2,500,000 shares outstanding. You can use the book value per share formula to help calculate the book value per share of the company. For example, let’s say that ABC Corporation has total equity of $1,000,000 and 1,000,000 shares outstanding. This means that each share of stock would be worth $1 if the company got liquidated. Although infrequent, many value investors will see a book value of equity per share below the market share price as a “buy” signal. But an important point to understand is that these investors view this simply as a sign that the company is potentially undervalued, not that the fundamentals of the company are necessarily strong.

No Comments